Each year a large amount of sulfur-containing acid gases Hydrogen Sulfide and Sulfur Dioxide is being generated worldwide as flue gases or involuntary harmful by-products of different industries: petroleum and natural gas production, power generation, metallurgy, chemical industry, cement production.
Due to adverse effects of hydrogen sulfide (H2S) and sulfur dioxide (SO2) on industrial processes, human health and the environment, it is necessary to remove these acid gases from all effluent streams.
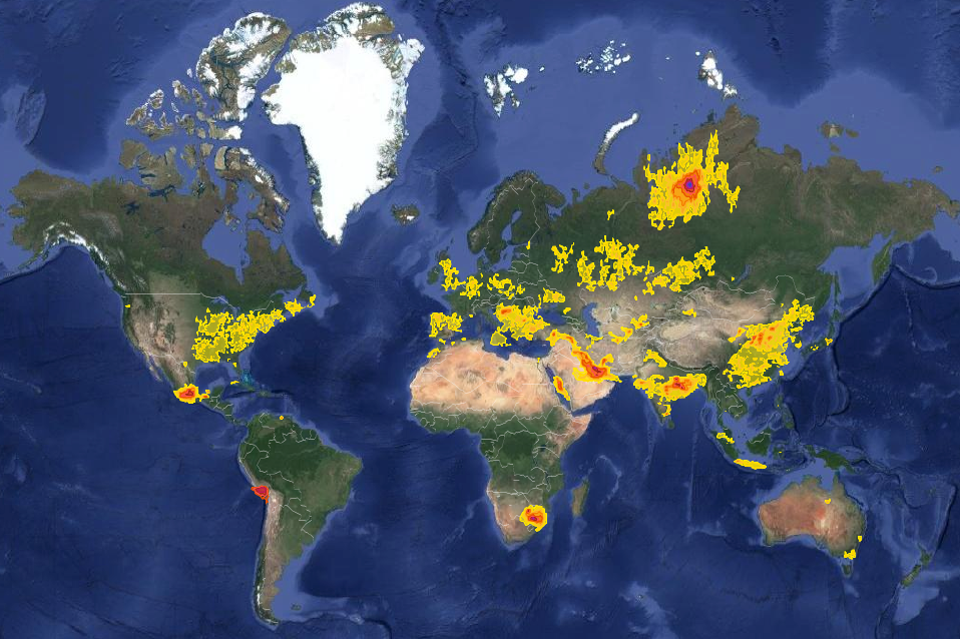
Screenshot of SO2 emission hotspot intensity map based on NASA OMI database.
Source: Greenpeace report “Global SO2 emission hotspot database”, 2019.
According to a Greenpeace report, power plants burning coal and oil along with refineries are responsible for two-thirds of the anthropogenic sulfur dioxide. Metals smelters are the other major sources worldwide.
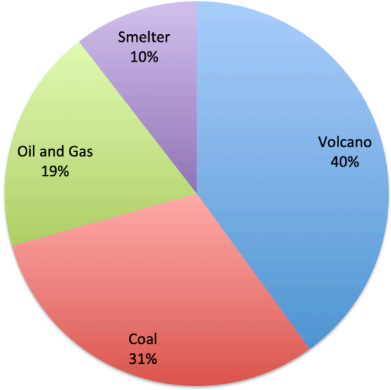
Sources identified by NASA OMI for SO2 emissions (kt/yr) across the world in 2018
The SO2 emissions from fossil fuel power generation and from oil and gas industry can be partially reduced in transition to reliable, affordable and sustainable energy supply.
The role of hydrocarbons declines as the world transitions to lower carbon energy sources. The path to a more sustainable energy is likely to lead to fundamental restructuring of the global energy system, and the renewable energy is likely to be the fastest growing source of energy over the next 30 years. The use of hydrogen grows significantly in accelerated and net zero scenarios. The production of hydrogen will be dominated by a mix of blue and green hydrogen, where blue hydrogen will be produced from fossil sources, when combined with Carbon Capture Use & Storage (“Energy Outlook, 2022”, BP).
However, according to OPEC and several major oil companies, it is most likely that the share of fossil fuels, especially natural gas, in the global energy mix will remain significant over decades.
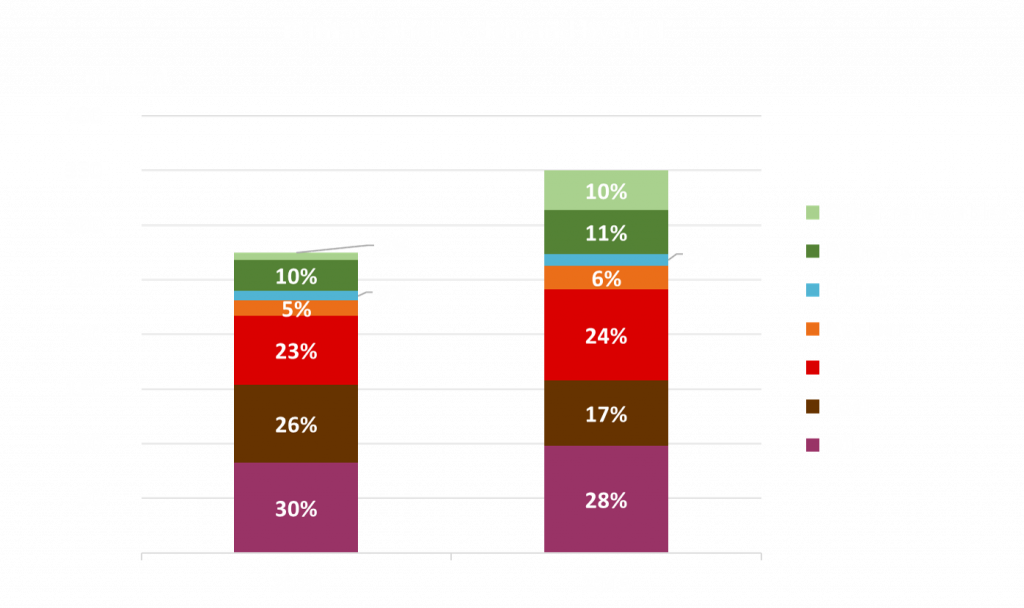
Source: OPEC World Oil Outlook 2045
At the same time, the further hydrocarbon production will be affected by changes in quality of Oil & Gas reserves and increasing sulfur content.
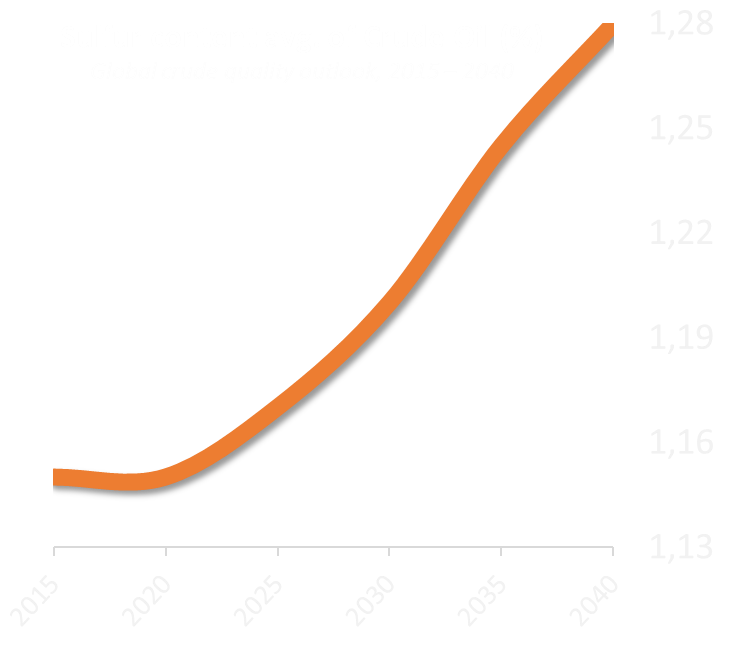
Source: OPEC
Climate change concern, more stringent environmental regulations, and the resulting need to remove sulfur-containing acid gases to ever-lower levels are among the factors that generate a great demand for flue gas desulfurization and sulfur recovery technologies.
There is a number of industrial processes for acid gas treatment, but they are CAPEX and OPEX intensive.
